Maintaining optimal CPU temperatures is crucial for ensuring your computer’s performance and longevity. Understanding what constitutes a good idle CPU temperature, the factors influencing it, and how to monitor and manage these temperatures can help prevent potential hardware issues.
Key Takeaways:
- An ideal idle CPU temperature typically ranges between 30°C to 40°C (86°F to 104°F).
- Factors such as ambient room temperature, computer case ventilation, and CPU cooler efficiency significantly impact idle temperatures.
- Regular monitoring and proper cooling practices are essential to maintain optimal CPU performance and longevity.
Understanding CPU Temperatures:
The CPU (Central Processing Unit) serves as the heart of your computer, handling computations and executing commands. As it operates, it generates heat, and maintaining this heat within acceptable limits is vital.
What Is Idle CPU Temperature?
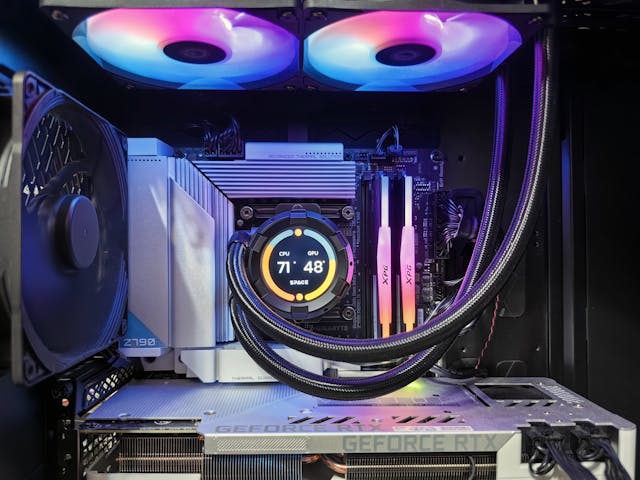

Idle CPU temperature refers to the heat level of your processor when it’s not under significant load—essentially when your computer is on but not performing demanding tasks. Monitoring idle temperatures provides a baseline to assess your system’s cooling efficiency.
Normal CPU Temperature Range:
For most CPUs, a normal idle temperature ranges between 30°C to 40°C (86°F to 104°F). Temperatures consistently above this range during idle periods may indicate inadequate cooling or other underlying issues.
| CPU Type | Normal Idle Temperature (°C) | Normal Idle Temperature (°F) |
|---|---|---|
| Intel CPUs | 30°C – 45°C | 86°F – 113°F |
| AMD CPUs | 35°C – 50°C | 95°F – 122°F |
| Overclocked CPUs | 40°C – 55°C | 104°F – 131°F |
Factors Affecting Idle CPU Temperature:
- Ambient Room Temperature:
- The surrounding environment plays a significant role. Higher room temperatures can lead to increased idle CPU temperatures. Maintaining a room temperature between 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) is generally recommended for optimal CPU performance.
- Computer Case Ventilation:
- Proper airflow within the computer case is crucial. Poor ventilation can trap heat, causing higher idle temperatures. Ensuring that intake and exhaust fans are functioning correctly and that there are no obstructions to airflow can help maintain optimal temperatures.
- CPU Cooler Efficiency:
- The effectiveness of your CPU cooler directly impacts temperature management. High-quality coolers dissipate heat more efficiently, keeping idle temperatures lower. Regular maintenance, such as cleaning dust from the cooler and reapplying thermal paste, can enhance cooling performance.
Monitoring and Managing Temperatures:
Regular monitoring of CPU temperatures allows for early detection of potential issues. Several software tools can assist in this process:
- HWMonitor: Provides real-time temperature readings and system information.
- Core Temp: Offers detailed CPU temperature data and logging capabilities.
- Open Hardware Monitor: Displays temperature sensors, fan speeds, and voltages.
Reducing High Temperatures:
If idle temperatures are consistently high, consider the following steps:
- Improve Case Airflow: Ensure that fans are correctly positioned and functioning. Consider adding additional fans or upgrading existing ones to enhance airflow.
- Upgrade the CPU Cooler: Investing in a more efficient cooler can significantly reduce temperatures.
- Reapply Thermal Paste: With time, thermal paste loses its effectiveness, impacting heat dissipation. Reapplying a high-quality thermal paste can improve heat transfer between the CPU and cooler.
- Maintain a Cool Environment: Keep your computer in a well-ventilated area away from heat sources.
Impact of Idle CPU Temperatures on Performance:
While idle temperatures may not directly affect performance, consistently high idle temperatures can be indicative of cooling issues that could lead to:
- Thermal Throttling: The CPU reduces its speed to prevent overheating, leading to decreased performance during demanding tasks.
- Reduced Lifespan: Prolonged exposure to high temperatures can degrade CPU components over time.
Optimal CPU Cooling Practices:
To maintain ideal CPU temperatures:
- Choose the Right CPU Cooler: Select a cooler appropriate for your CPU’s thermal output. High-performance CPUs may require advanced cooling solutions like liquid cooling.
- Regular Maintenance: Clean dust from components, ensure fans are operational, and check for any signs of wear.
- Cable Management: Organize cables to prevent obstruction of airflow within the case.
CPU Manufacturer-Specific Temperature Considerations:
Different CPU manufacturers have varying specifications:
- AMD CPUs: Modern AMD processors are designed to operate efficiently at higher temperatures. However, maintaining idle temperatures within the recommended range is still essential.
- Intel CPUs: Intel processors typically have lower thermal thresholds. Ensuring adequate cooling is crucial to prevent thermal throttling.
Advanced Temperature Management:
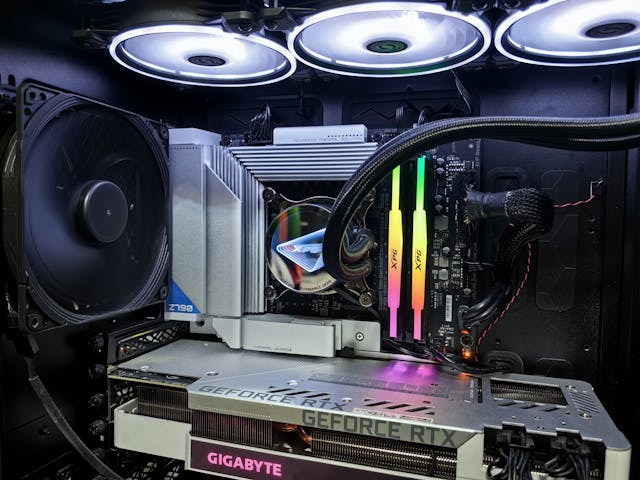

For enthusiasts looking to optimize performance:
- Overclocking: Increasing CPU clock speeds can lead to higher temperatures. Adequate cooling solutions are necessary to manage this additional heat.
- Custom Cooling Solutions: Implementing custom liquid cooling loops can provide superior temperature control for high-performance systems.
Frequently Asked Questions:
- What is the optimal idle temperature range for a CPU?
- A safe idle temperature is typically between 30°C to 40°C (86°F to 104°F).
- At what idle temperature should CPU overheating become a concern?
- If idle temperatures consistently exceed 50°C (122°F), it’s advisable to inspect your cooling system.
- How does the surrounding room temperature influence idle CPU heat levels?
- Higher ambient temperatures can raise idle CPU temperatures, as the cooling system relies on the surrounding air to dissipate heat.
- What factors contribute to higher-than-normal idle CPU temperatures?
- Poor case ventilation, inefficient CPU coolers, degraded thermal paste, and high ambient temperatures are common contributors.
- Can an unusually high idle CPU temperature signal potential hardware problems?
- Yes, if your CPU is running at an unusually high idle temperature, it could indicate several potential issues. These may include dust buildup in the cooling system, a failing CPU fan, dried-out thermal paste, or even background applications overusing the CPU. Regular monitoring and maintenance can help prevent long-term damage.
- What are the differences in idle CPU temperatures between desktops and laptops?
- Desktops generally have better cooling systems due to larger cases and better airflow, allowing for lower idle temperatures (30°C to 40°C).
- Laptops, on the other hand, have compact cooling solutions, which can result in higher idle temperatures (40°C to 50°C). High-performance gaming laptops may idle even more due to powerful CPUs and limited ventilation.
- What are the recommended safe temperature limits for a CPU under workload?
- When a CPU is under load (such as gaming, video editing, or rendering), its temperature will naturally rise. The general safe range is:
- Intel CPUs: 60°C – 85°C
- AMD CPUs: 65°C – 90°C
- If temperatures exceed 90°C, your CPU may start thermal throttling, which reduces performance to prevent overheating.
- When a CPU is under load (such as gaming, video editing, or rendering), its temperature will naturally rise. The general safe range is:
- At what temperature does GPU overheating become a serious concern?
- GPUs generally tolerate higher heat levels than CPUs. For most GPUs, an optimal temperature range is:
- Idle: 35°C – 55°C
- Under load: 70°C – 85°C
- If your GPU exceeds 90°C under load, you should check for proper ventilation, thermal paste quality, and dust buildup.
- GPUs generally tolerate higher heat levels than CPUs. For most GPUs, an optimal temperature range is:
- What is the ideal temperature range for a CPU during everyday usage?
- For general tasks like web browsing and document editing, your CPU should stay within:
- Intel CPUs: 35°C – 55°C
- AMD CPUs: 40°C – 60°C
- If your CPU is consistently above 60°C during light tasks, it may indicate insufficient cooling.
- For general tasks like web browsing and document editing, your CPU should stay within:
- What temperature threshold is considered too high for a GPU during intense graphics processing?
- When playing games or using heavy GPU workloads, anything above 90°C is considered dangerous. If your GPU reaches this level, check:
- Fan speeds (increase if needed)
- Airflow in your case
- Replacing thermal paste
- Cleaning dust buildup
- When playing games or using heavy GPU workloads, anything above 90°C is considered dangerous. If your GPU reaches this level, check:
- What key factors impact the typical operating temperatures of a CPU and GPU?
- Multiple elements contribute to CPU and GPU heat levels, including:
- Cooling system efficiency (air vs. liquid cooling)
- Thermal paste quality and application
- Room temperature
- Overclocking settings
- Background applications and software load
- Multiple elements contribute to CPU and GPU heat levels, including:
- Can prolonged high temperatures negatively affect the lifespan of a CPU or GPU?
- Yes, extended exposure to excessive heat can shorten the lifespan of your components.
- Effects on CPU: Thermal degradation, slower performance, and potential failure over time.
- Effects on GPU: Artifacting (visual glitches), instability, and increased risk of permanent damage.
- Solution: Keep your system well-ventilated, reapply thermal paste every 1-2 years, and clean dust regularly.
Final Thoughts
Keeping your CPU’s idle temperature within a safe range is essential for both performance and durability. Regular monitoring, proper cooling solutions, and preventive maintenance will help keep your CPU running at optimal temperatures. Whether you use air cooling, liquid cooling, or custom solutions, ensuring good airflow and checking thermal performance can prevent overheating and improve system stability.
For better optimization, always:
- Use high-quality thermal paste
- Ensure proper airflow in your case
- Monitor temperatures regularly
- Upgrade cooling solutions if necessary
By following these best practices, you can maintain a healthy and efficient computing system for years to come!